BRCA: The Breast Cancer Gene
What Is A Gene?
Each person’s DNA contains the code used to build the human body and keep it functioning. Genes are the small sections of DNA that code for individual traits. For example, someone with naturally red hair has a gene that causes his or her hair to be red.
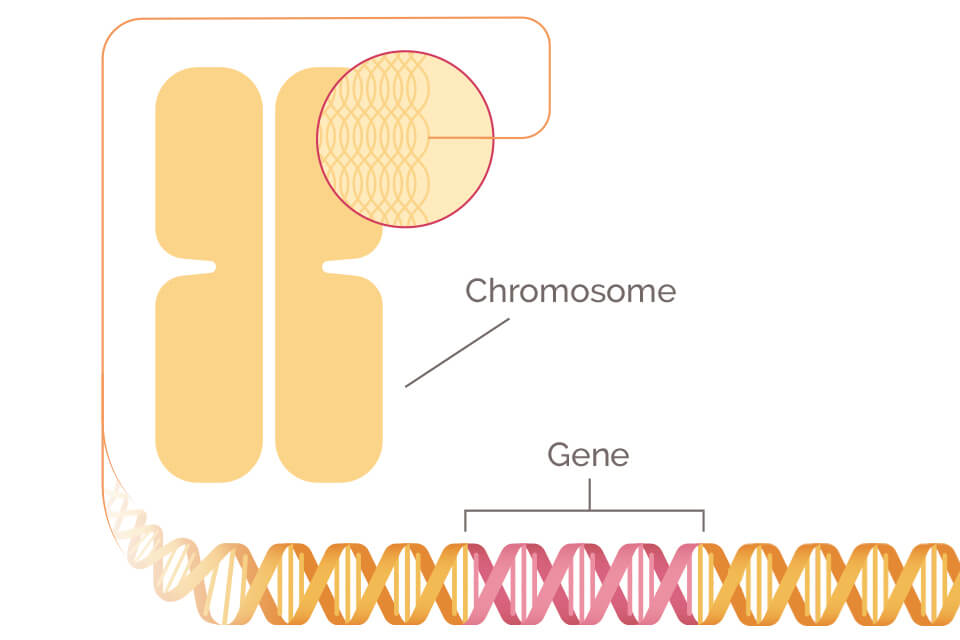
All inherited traits are passed down through genes. Each person has two copies of every gene: one gene from each parent. Since each parent passes down exactly half of their genes to each child, any of the parent’s genetic traits has a 50% chance of being passed on to their offspring.
What Is BRCA?
The name “BRCA” is an abbreviation for “BReast CAncer gene.” BRCA1 and BRCA2 are two different genes that have been found to impact a person’s chances of developing breast cancer.
Every human has both the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. Despite what their names might suggest, BRCA genes do not cause breast cancer. In fact, these genes normally play a big role in preventing breast cancer. They help repair DNA breaks that can lead to cancer and the uncontrolled growth of tumors. Because of this, the BRCA genes are known as tumor suppressor genes.
However, in some people these tumor suppression genes do not work properly. When a gene becomes altered or broken, it doesn’t function correctly. This is called a gene mutation.
BRCA Mutations
A small percentage of people (about one in 400, or 0.25% of the population) carry mutated BRCA1 or BRCA2 genes. A BRCA mutation occurs when the DNA that makes up the gene becomes damaged in some way.
When a BRCA gene is mutated, it may no longer be effective at repairing broken DNA and helping to prevent breast cancer. Because of this, people with a BRCA gene mutation are more likely to develop breast cancer, and more likely to develop cancer at a younger age. The carrier of the mutated gene can also pass a gene mutation down to his or her offspring.
BRCA Mutation Risks
It is estimated that one in eight women, or approximately 12%, will be diagnosed with breast cancer in her lifetime.
However, women with certain genetic mutations have a higher lifetime risk of the disease. It’s estimated that 55 – 65% of women with the BRCA1 mutation will develop breast cancer before age 70.
Approximately 45% of women with a BRCA2 mutation will develop breast cancer by age 70.
Women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation who overcome their breast cancer with treatment appear to have a higher-than-average chance of developing a second cancer. This is called a recurrence. Cancers related to a BRCA1 mutation are also more likely to be triple negative breast cancer, which can be more aggressive and difficult to treat.
You may find these statistics alarming. However, it’s important to note that less than 10% of women diagnosed with breast cancer have a BRCA mutation. Also, with early detection, the vast majority of breast cancer cases can be successfully treated—and that’s true even for people who have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation.
Reducing Risks Associated with BRCA Gene Mutations
If you discover you have a BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene mutation, there are preventative measures you can take to help reduce your risk of developing breast cancer in the future. One of these measures may be taking a form of hormone therapy, such as tamoxifen. Another preventative measure may include taking a surgical prevention approach, such as a bilateral prophylactic mastectomy. This involves removing the breast tissue as a preventative measure, before cancer develops, and is usually done along with breast reconstruction. Some women may also opt to have their ovaries and fallopian tubes removed since BRCA gene mutations increase the risk of developing ovarian cancer as well. However, you should discuss all options available to you, and the benefits and risks of each, with your healthcare provider.



