Stage 1 Breast Cancer Overview
Stage 1 breast cancer explained
Stage 1 breast cancer is the earliest stage of what is considered invasive breast cancer. But what exactly does “invasive” mean? Invasive breast cancer indicates that the cancer is no longer contained in its original location.
In Stage 1 breast cancer, cancerous cells have spread beyond the original location they began in the breast to the surrounding normal tissue or lymph nodes. The spread is generally contained to a small area.
Stage 1 breast cancer is considered early-stage cancer and is highly treatable and survivable. The five-year relative survival rate for breast cancer found and treated in the localized stage is over 99%, according to the American Cancer Society.
Learn more about breast cancer stages.
What is Stage 1 breast cancer?
Whereas Stage 0 is non-invasive breast cancer, Stage 1 breast cancer is invasive breast cancer. Stage 1 invasive breast cancer is early-stage breast cancer, where tumors are generally small and found to be in the early stages when it can be most effectively treated.
Stage 1 invasive breast cancer is classified into two categories—Stage 1A or Stage 1B—based on the size of the tumor and whether it is only in the breast tissue or has spread to the lymph nodes.
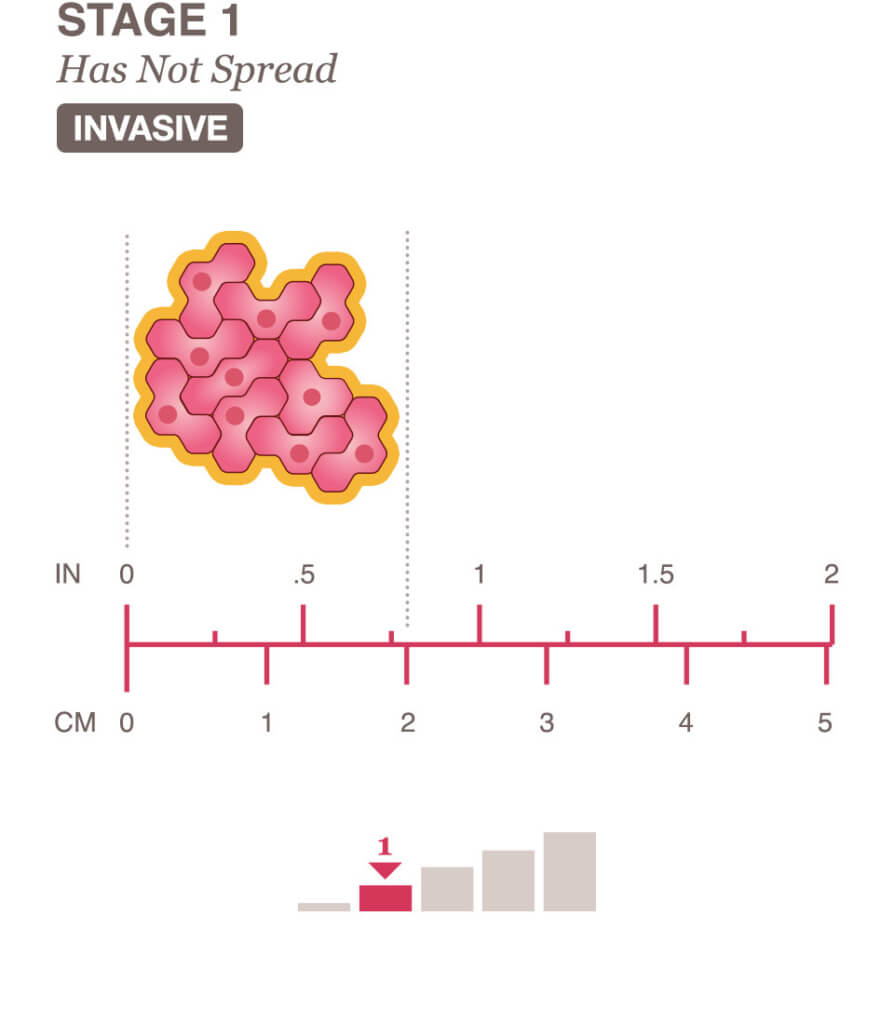
Stage 1A breast cancer
In Stage 1A breast cancer, the tumor is 2 centimeters or smaller (smaller than the size of a peanut) and has not spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage 1B breast cancer
When breast cancer spreads, it typically spreads to the lymph nodes close to the breast first. Therefore, Stage 1B breast cancer implies that there is lymph node involvement. This means that at least one lymph node has evidence of cancer due to the presence of small clusters of abnormal (cancerous) cells between the size of a pinprick to the width of a grain of rice (0.2mm to 2.0mm).
Most times in Stage 1B, a small cancerous tumor (2 centimeters or smaller) is found in the breast, in addition to cancerous cells in the lymph nodes.
Other times, there is no actual tumor found in the breast of a person with Stage 1B breast cancer; instead, cancerous cells are found only within the lymph nodes close to the breast.
Stage 1 breast cancer signs and symptoms
Stage 1 breast cancer may present with symptoms or not. If symptoms are present, Stage 1 signs of breast cancer may include:
- A lump in the breast (this is the most common Stage 1 symptom)
- Nipple discharge, including bloody or clear fluid
- Inversion (turning inward) or flattening of the nipple
- Dimpling of the skin
- Changes to breast skin texture
- Changes in the size or shape of breast
- Redness or swelling
Stage 1 breast cancer diagnosis
Stage 1 breast cancer is typically discovered in one of two ways. The first way is through a routine screening mammogram when no symptoms are present. The second way is through a diagnostic mammogram and ultrasound following the appearance of symptoms or an abnormal finding in a breast self-exam or clinical breast exam.
Mammogram for Stage 1 breast cancer
A mammogram is often the best option for detecting breast cancer in its earliest stages. This low-dose x-ray is performed with a machine that has two plates that flatten the breast and spread the tissue apart, providing a clearer picture of the breast.
There are two types of mammograms. A screening mammogram is administered at a routine mammogram appointment in women who have no apparent signs or symptoms of breast cancer present.
A diagnostic mammogram is administered if the screening mammogram showed an abnormal result or if there are signs of breast cancer present. A diagnostic mammogram can look for breast cancer and help doctors determine both diagnosis and staging.
Mammogram 101
Learn what to expect and how to prepare for a mammogram in the free eBook, Mammogram 101.
Get the Free eBookBreast ultrasound for Stage 1 breast cancer
To determine a Stage 1 breast cancer diagnosis, doctors may also recommend a breast ultrasound, which uses sound waves to view the inside of the breasts. The ultrasound generates a picture called a sonogram, which can help measure the size and location of a breast lump and determine if it is a cyst, which is not typically cancerous, or another benign finding.
If you are experiencing any potential Stage 1 breast cancer symptoms, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider to discuss symptoms and signs, testing, and potential diagnosis.
Stage 1 breast cancer treatment
Stage 1 breast cancer treatment typically includes surgery, radiation, or a combination of treatments.
Stage 1 breast cancer treatment guidelines are based on several factors, including age at diagnosis, personal health history, genetic risk, and more. Treatment options continue to evolve and improve, with many patients opting for a combination of Stage 1 breast cancer treatments.
Surgery
There are three common types of Stage 1 breast cancer surgery: lumpectomy, mastectomy, and sentinel lymph node removal.
Lumpectomy, or breast-conserving surgery, is the most common surgical treatment for Stage 1 breast cancer since the tumor is small. A lumpectomy removes the cancerous tissue, a small margin of healthy tissue around it, and affected lymph nodes, if needed. Lumpectomy is often followed by radiation to reduce the chance of the cancer coming back.
For Stage 1 breast cancer that has spread further or if a lumpectomy can’t remove all of the cancerous cells, a mastectomy to remove the entirety of the breast tissue may be recommended.
Finally, doctors may also consider lymph node removal if the Stage 1 breast cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. However, many early-stage breast cancer patients are now given radiation instead of lymph node removal surgery.
Questions about breast cancer surgery?
Read more about surgical options, including breast reconstruction and healing after surgery in this free eBook.
Breast Cancer Surgery eBookRadiation
Radiation is standard of care after a lumpectomy for Stage 1 breast cancer. Radiation may be used after a mastectomy if the tumor was large, margins were positive, cancer was found in a lymph node, or other high-risk features were present.
For this treatment option, the breast tissue and lymph nodes are treated with cancer-killing radiation therapy for several weeks at a hospital, radiation center, or other outpatient facility.
Common radiation side effects include fatigue, skin irritation (redness, peeling, or itchiness), and swelling of the breast or arm.
Hormonal therapy
Depending on the type of cancer cells found and additional risk factors, a hormonal therapy regimen is sometimes used to treat Stage 1 breast cancer. Tamoxifen, a daily pill, is the most common hormonal therapy for those with hormone receptor-positive breast cancer after radiation or surgery. Women who are post-menopausal may take an aromatase inhibitor instead. Hormone therapy can be used for 5-10 years after a lumpectomy or mastectomy to decrease the risk of recurrence.
Biologic targeted therapy
More recent biologic targeted therapies for Stage 1 breast cancer attack breast cancer cells and come with fewer side effects. Targeted cancer therapy, which uses drugs to block the growth of cancer cells, can be used in conjunction with other Stage 1 breast cancer treatments.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is rarely used to treat Stage 1 breast cancer or other early stages of cancer. However, in some cases, chemotherapy may be used to treat Stage 1 breast cancer, or it may be used after surgery to reduce the chances of the cancer coming back. Always consult with your healthcare team for the treatment plan that is right for you.
Bone strengthening treatment
Bone-density medications, called bisphosphonates, are not a treatment for cancer, but they can help prevent bone loss during breast cancer treatment. These treatments may also reduce the risk of recurrence for those with Stage 1 breast cancer. Risks can include heart disease and kidney issues.
Breast cancer survivors have a significantly higher risk of osteoporosis and osteopenia, and some treatments increase the risk of fractures. Talk with your doctor about bone health and recommendations for bone strengthening.
Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate
Early-stage breast cancer is very treatable, and the Stage 1 breast cancer survival rate is high. In the U.S., the 5-year relative survival rate for Stage 1 breast cancer is over 99%, according to the American Cancer Society.
Breast cancer survival rates can vary based on the type of cancer, stage and grade, age at diagnosis, overall health, and more. You can further discuss Stage 1 breast cancer prognosis with your healthcare provider.
Life after Stage 1 breast cancer
Earlier stage breast cancers, such as Stage 1 breast cancer, are treatable and survivable. Life after Stage 1 breast cancer can be full and long.
Your healthcare provider may encourage additional screenings, and it is always important to pay attention to your physical and mental health by staying active, eating a healthy diet, eliminating or limiting alcohol consumption, meditating, and maintaining relationships. NBCF offers support at every step of your breast cancer journey, including a wealth of resources such as patient navigators, support groups, HOPE Kits, and access to free educational guides.
Stage 1 breast cancer FAQs
Is Stage 1 breast cancer curable?
While you are not likely to hear a doctor use the word “curable,” they may use the term “cancer-free.” Stage 1 breast cancer has many options for treatment and an excellent prognosis for recovery and becoming “cancer-free.”
Can Stage 1 breast cancer spread to the bones?
If left undetected or untreated, Stage 1 breast cancer can grow and spread. If breast cancer spreads to the bones, it is no longer Stage 1. Breast cancer that has spread to the bones is Stage 4 metastatic breast cancer. However, Stage 1 breast cancer carries an excellent prognosis when treated appropriately.
What are the types of breast cancer recurrence?
While it is rare for Stage 1 breast cancer to recur, it is important to be aware of the different levels of breast cancer recurrence. There are three levels of breast cancer recurrence:
| Type of Recurrence | Indication |
| Local | Breast cancer returns in the same breast as the original tumor |
| Regional | Breast cancer returns near the original site, in lymph nodes in the armpit or collarbone |
| Distant | Breast cancer spreads away from the original tumor to other parts of the body, such as lungs, liver, bones, or brain |
Learn more with NBCF’s free Breast Cancer Recurrence eBook.
Where can I turn to for breast cancer education?
NBCF’s mission is to provide help and inspire hope to those impacted by breast cancer. Please visit our Breast Cancer Resources page to download free educational guides, get information on the NBCF National Mammography Program and Patient Navigation Program, information on financial support, and more.
Sources:
National Cancer Institute



