Chemotherapy
What is chemotherapy?
Chemotherapy is a treatment method that uses a combination of drugs to either destroy cancer cells or slow down the growth of cancer cells.
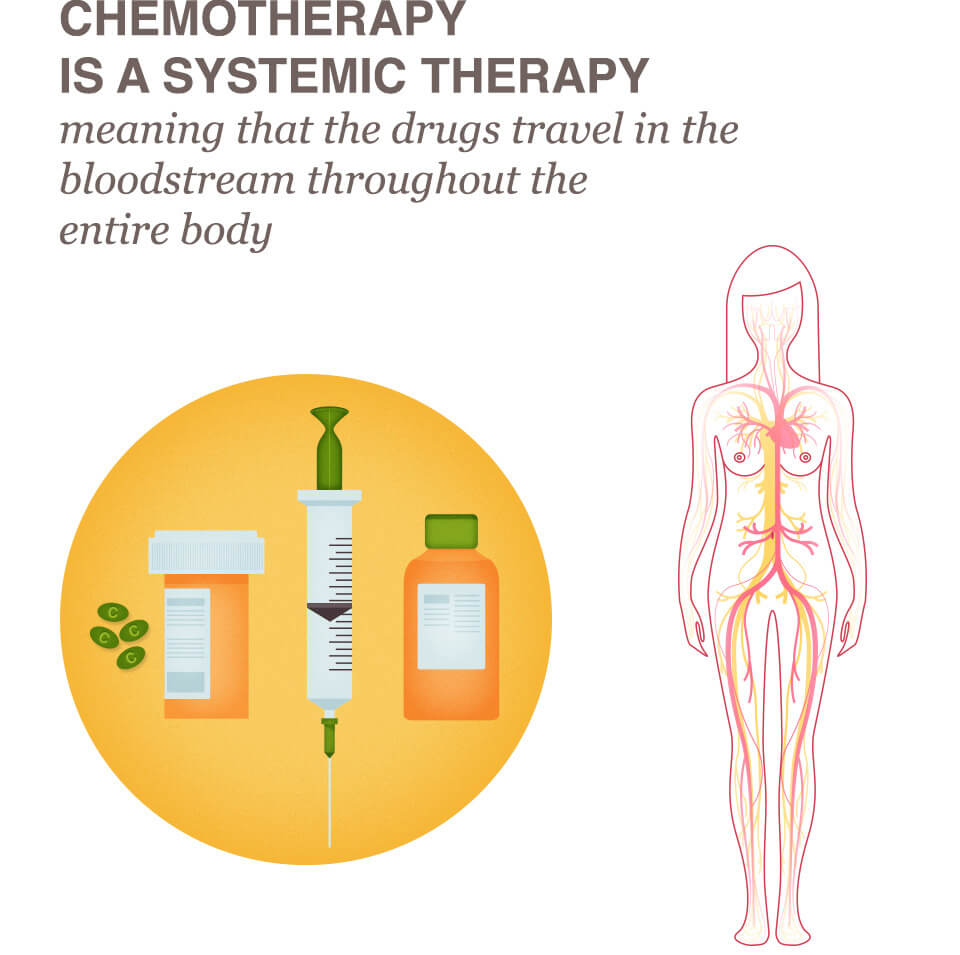
- Cytotoxic drugs (meaning “toxic to cells”) are usually given orally or through a vein (intravenously or “through the bloodstream”).
- Chemotherapy is a systemic therapy, meaning that the drugs travel in the bloodstream throughout the entire body.
Who needs breast cancer chemotherapy?
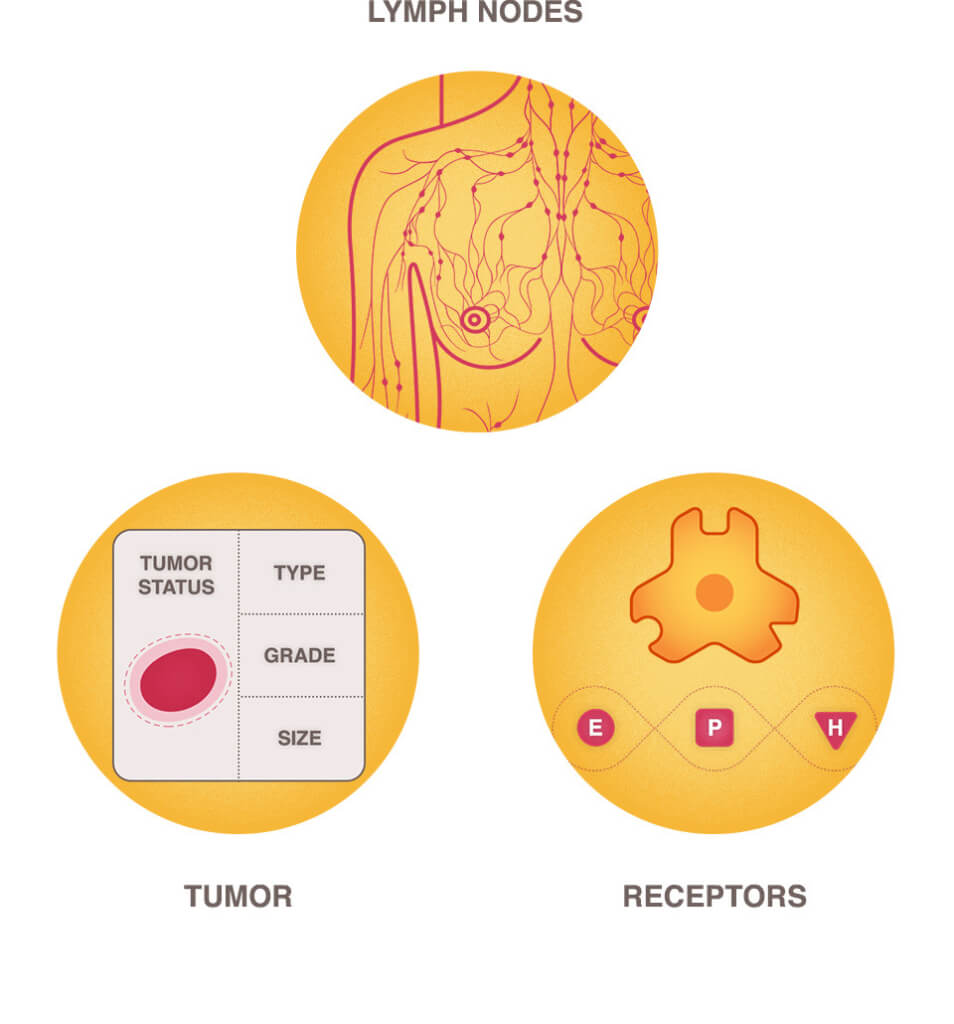
Chemotherapy is offered to most patients based on several factors, including:
- Tumor type
- Tumor grade
- Tumor size
- Type of receptors and status
- Number of lymph nodes involved and degree of involvement
- The risk of cancer spreading elsewhere in the body
Your medical team will work to select the right blend of chemotherapy drugs to suppress each stage of the cancer cells’ growth.
How is breast cancer chemotherapy administered?
Chemotherapy is commonly prescribed along with other treatment methods such as hormonal and targeted therapies. It can also be used to shrink a tumor before surgery for easier and safer removal, referred to as neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Most chemotherapy treatments are administered intravenously, or through an IV.
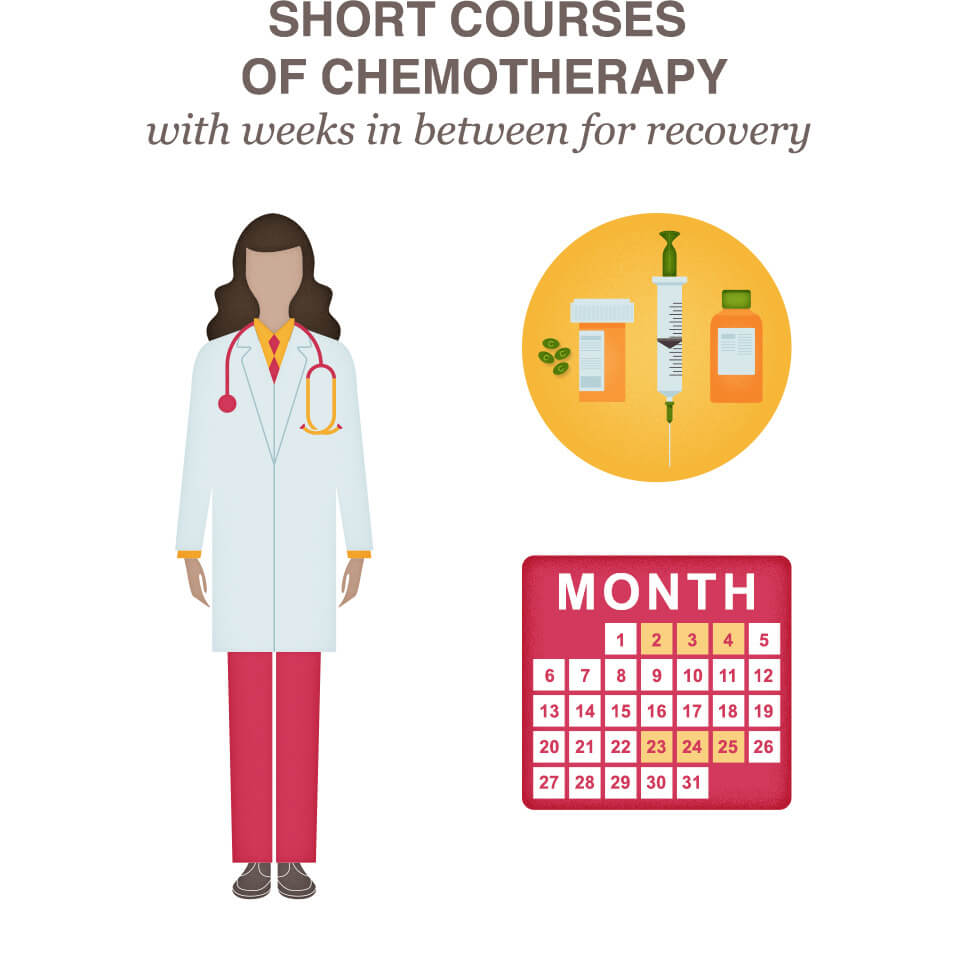
If you receive chemotherapy, your doctor will administer it in short courses with several weeks in between to allow your normal cells to recover. This treatment period can be a challenging time, both emotionally and physically. It is important for you to develop a support team of family or friends who can help comfort and encourage you during this time.
As you begin chemotherapy, make your treatment team aware of any upcoming significant milestones, such as weddings or graduations. Your treatments can keep these important milestones in mind when planning your treatment timeline so you can feel your best when the events occur.
What are the side effects of chemotherapy?
Although chemotherapy kills the fast-growing cancer cells, the drugs can also, unfortunately, harm normal cells that divide rapidly.
Chemotherapy side effects may include:
- Reduction in red blood cells: When chemotherapy drugs lower the levels of healthy blood cells, you’re more likely to get infections, bruise or bleed easily, and feel very weak and tired. Your healthcare team will check for low levels of red blood cells. If your levels are low, your healthcare team may stop the chemotherapy for a while or reduce the dose of the drug. There are also medicines that can help your body make new red blood cells.
- Reduction in white blood cells: A reduction in white blood cells can increase your risk of getting an infection. This is why it’s important to avoid people who have a cold or flu, eat healthy meals, get your rest, and take your temperature each day. A rise in body temperature is usually the first sign that your white blood cells are low. When your white blood cells are low, it is called neutropenia. There are medications your medical oncologist can prescribe to get your white blood cells to start increasing in number again.
- Hair loss: Chemotherapy can affect the cells that produce hair and may cause hair loss. If you lose your hair during chemotherapy, it will grow back after treatment, but the color and texture may be changed. Read more about hair loss during chemotherapy and head covering options in Wigs for Cancer Patients: Your Guide to Finding the Right Wig.
- Intestinal changes: Chemotherapy can disrupt the balance of cells lining your intestinal tract, leading to poor appetite, nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, or mouth and lip sores. Your healthcare team can prescribe medicines, such as anti-nausea drugs, and suggest other ways to help with these problems. For example, your healthcare team might recommend you stick to eating certain foods that can help you during cancer treatment.
- Peripheral neuropathy: Some chemotherapy drugs can affect nerve cells, causing tingling or numbness in the hands or feet. This side effect is called peripheral neuropathy. This usually goes away after treatment is over.
Are there any lasting side effects of chemotherapy?
Sometimes people do experience problems that may not go away. For example, some of the drugs used for breast cancer may weaken the heart. Your doctor may check your heart before, during, and after treatment. A rare side effect of chemotherapy is that occasionally, years after treatment, a few women have developed leukemia (cancer of the blood cells).
Some chemotherapy drugs may cause your menstrual periods to be irregular or stop altogether (menopause). Chemotherapy can damage the ovaries. If you have not gone through menopause yet, you may have hot flashes or experience sexual side effects, such as vaginal dryness. Read more about sexual side effects and management in Sexual Health and Breast Cancer: A Healing, Intimacy, and Hope Guide.
Fertility after completing chemotherapy treatments
Some chemotherapy drugs may cause infertility in women of childbearing age because it can affect the ovaries, preventing normal ovarian function in the future. If you are of childbearing age and plan to have children in the future, you should talk with your doctor about family planning and fertility preservation before treatment begins. Learn more about how breast cancer treatment can affect future fertility in Does Breast Cancer Treatment Affect Fertility?
Although chemotherapy is often a very personally challenging time in life, there are thousands of people today who are very thankful for its life-saving and life-extending potential.



